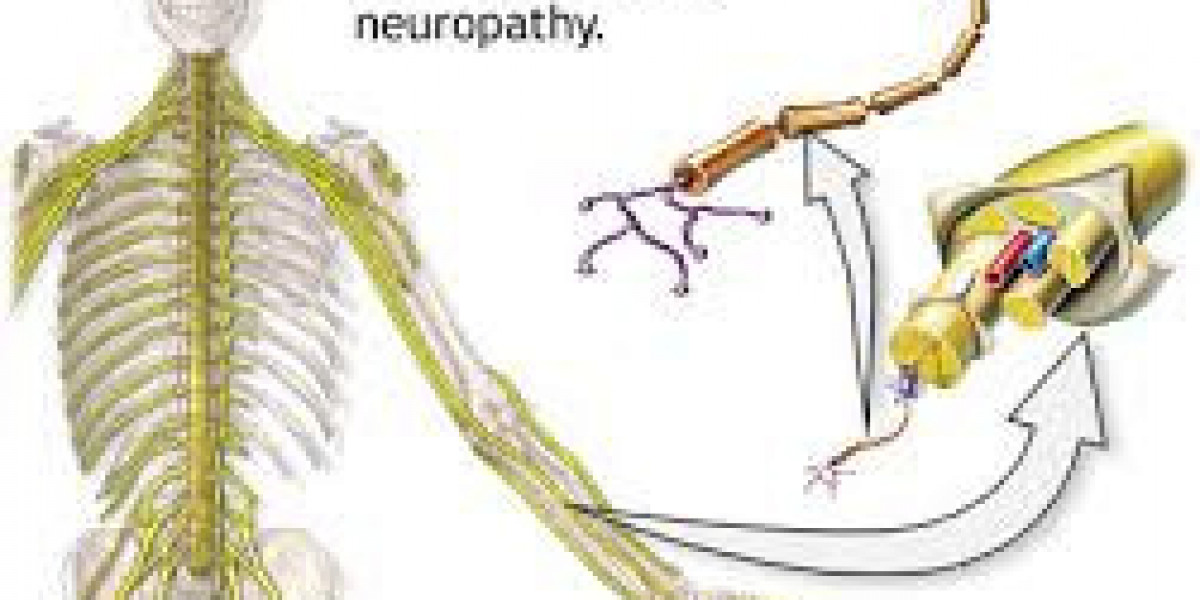
Diabetes doesn’t just affect blood sugar levels; over time, it can also damage nerves throughout the body—a condition known as diabetic neuropathy. This nerve damage can cause numbness, pain, tingling, and weakness, most often in the feet and hands. Fortunately, there are effective ways to manage this condition and improve your quality of life. In this guide, you will learn how to recognize symptoms, understand causes, and explore treatment options including medications like Pregabalin 300 mg.
Understanding Diabetes-Related Nerve Damage
Diabetic neuropathy is a common complication of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. High blood glucose levels over extended periods can injure nerves and interfere with their ability to send signals. As a result, nerve damage can occur in different areas of the body, causing various symptoms depending on the type of neuropathy involved.
There are four main types of diabetic neuropathy:
Peripheral neuropathy – Affects feet, legs, hands, and arms.
Autonomic neuropathy – Impacts internal organs like the heart, stomach, and bladder.
Proximal neuropathy – Causes pain in the thighs, hips, or buttocks.
Focal neuropathy – Appears suddenly and affects specific nerves, often in the head or torso.
Early intervention is key to managing these symptoms and preventing further complications.
Common Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
If you have diabetes, be on the lookout for these symptoms of nerve damage:
Numbness or reduced ability to feel pain or temperature changes
Tingling or burning sensations
Sharp pains or cramps, especially at night
Muscle weakness
Foot problems, such as ulcers or infections
Recognizing these signs early can help you seek treatment and minimize long-term damage.
Causes Behind Diabetic Nerve Damage
The root cause of diabetic neuropathy is sustained high blood sugar. However, other factors may also play a role, such as:
High cholesterol and triglycerides
Smoking and excessive alcohol use
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Chronic inflammation from autoimmune responses
Moreover, genetic predisposition can make some individuals more likely to develop neuropathy.
How to Diagnose Diabetic Neuropathy
Healthcare professionals use several diagnostic tools to confirm diabetic neuropathy. These include:
Physical exams – Checking for sensitivity to touch, temperature, and vibration.
Nerve conduction studies – Measuring how quickly nerves send signals.
Electromyography (EMG) – Assessing muscle response to nerve stimulation.
Autonomic tests – Monitoring heart rate and blood pressure changes.
An accurate diagnosis allows for more targeted and effective treatment strategies.
Effective Strategies to Manage Diabetes-Related Nerve Damage
While diabetic nerve damage is not reversible, you can manage its symptoms and slow its progression. Here are key strategies to consider:
1. Keep Blood Sugar Levels Under Control
The most critical step is maintaining optimal blood sugar levels. Consistently high glucose can worsen nerve damage, while good control can prevent further deterioration. To manage blood sugar effectively:
Monitor levels regularly
Follow a diabetic-friendly diet
Exercise regularly
Take prescribed medications as directed
2. Relieve Nerve Pain with Medication
Several medications can help manage the pain associated with diabetic neuropathy. Among the most effective options is Pregabalin 300 mg, which is FDA-approved for treating nerve pain due to diabetes.
Pregabalin 300 mg works by calming overactive nerves, reducing pain signals sent to the brain. Patients often report significant relief from burning, tingling, and sharp pains when using this medication. Additionally, it may help improve sleep quality and reduce anxiety often linked with chronic pain.
Other medications used include:
Gabapentin
Duloxetine
Amitriptyline
Capsaicin cream (topical)
However, always consult your doctor before starting any new treatment.
3. Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle
A balanced lifestyle supports better nerve health and overall well-being. Key habits include:
Regular exercise – Boosts blood flow to the nerves and reduces inflammation.
Quit smoking – Smoking narrows blood vessels, limiting oxygen to nerves.
Limit alcohol – Excessive drinking can worsen nerve damage.
Eat a nutrient-rich diet – Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
4. Take Care of Your Feet
Foot problems are common in people with diabetic neuropathy, especially when there's reduced sensation. To prevent complications:
Inspect your feet daily for blisters, cuts, or infections
Wash and moisturize feet regularly
Wear comfortable, protective footwear
Avoid walking barefoot, even indoors
If you notice any wounds or changes, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
5. Try Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help improve muscle strength, balance, and mobility. In addition to standard exercises, therapists may use:
Electrical stimulation therapy
Balance training
Gait analysis and improvement
This approach not only reduces pain but also helps prevent falls and injuries.
6. Consider Alternative Therapies
Some patients find relief through alternative treatments such as:
Acupuncture – May relieve pain by stimulating specific nerve points.
Biofeedback – Teaches relaxation techniques to control pain responses.
Mindfulness and meditation – Reduces the emotional toll of chronic pain.
While these methods aren’t a replacement for medication like Pregabalin 300 mg, they can complement your treatment plan.
Importance of Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up
Managing diabetic neuropathy requires ongoing care. Regular checkups with your healthcare provider help track progress, adjust medications, and prevent complications. Additionally, staying up to date with eye, kidney, and heart screenings is essential for comprehensive diabetes care.
When to Talk to Your Doctor
You should seek medical attention if:
You experience new or worsening symptoms
Pain becomes unmanageable
You notice sores or infections that don't heal
Balance or coordination issues interfere with daily activities
Your doctor may adjust your medications, including the dosage of Pregabalin 300 mg, or recommend additional testing to assess nerve function.
The Role of Pregabalin 300 mg in Long-Term Pain Relief
Many doctors prescribe Pregabalin 300 mg for patients experiencing moderate to severe diabetic nerve pain. Its benefits include:
Quick symptom relief
Improved sleep and reduced anxiety
Minimal drug interactions
However, some side effects may occur, including dizziness, weight gain, or blurred vision. Discuss any side effects with your healthcare provider to weigh the pros and cons.
Most importantly, never stop or adjust the dosage without professional guidance, as this can lead to withdrawal symptoms or rebound pain.
Conclusion: Take Control of Diabetic Nerve Damage Today
Diabetic neuropathy may be a serious complication, but it doesn’t have to control your life. By managing blood sugar, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and using effective treatments like Pregabalin 300 mg, you can significantly reduce symptoms and improve your daily comfort.
Consistency and commitment are key. With the right tools and support, you can stay ahead of diabetic nerve damage and enjoy a higher quality of life. Don’t wait—start taking proactive steps toward better nerve health today.